In this post i would like to list out the various methods to extract the time from DATETIME data type in SQL Server. Depends on the version of the SQL Server you need to use different methods. In SQL Server 2008 you can use any of these methods but in SQL Server 2005 and SQL Server 2000 only method 1,2 and 3 will work.
DECLARE @DT DATETIME
SET @DT = GETDATE()
-- Method 1:
SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(30),@DT,114)
Output:------------------------------
22:31:43:047
(1 row(s) affected)
-- Method 2:
SELECT CAST(@DT AS TIME)
Output:----------------
22:31:43.0470000
(1 row(s) affected)
-- Method 3:
SELECT DATEADD(DAY, DATEDIFF(DAY, @dt, 0), @dt)
Output:-----------------------
1900-01-01 22:31:43.047
(1 row(s) affected)
-- Method 4:
SELECT @DT - CAST(FLOOR(CAST(@DT AS FLOAT)) AS DATETIME)
Output:
-----------------------
1900-01-01 22:31:43.047
(1 row(s) affected)
Reference : Vijaya Kadiyala (www.DotNetVJ.com)
Wednesday, February 10, 2010
Extract Just Time from DATETIME data type in SQL Server 2000, SQL Server 2005 and SQL Server 2008
sargable vs non-sargable queries
A condition in a query is said to be sargable if the SQL Server can take the advantage of an index to speed up the execution of the query (using index seeks, not covering indexes). sargable stands for Search ARGument Able.
Non-sargable search arguments in the WHERE clause are:
IS NULL
"<>"
NOT
NOT EXISTS
NOT IN
NOT LIKE
LIKE '%something'
In a query if you have mix of Non-sargable and Sargable conditions then SQL Server might use covering index based on the columns used in SELECT Clause, WHERE Clause and JOIN clause. These covering indexes sometimes may not be appropriate to the query and can increase disk I/O. In adidtion to this, try to avoid using any functions on Indexed columns.
Non-sargable Query:
SELECT FirstName,LastName FROM Person.Person WHERE LEFT(LastName,2) = 'Ma'
Sargable Query:
SELECT FirstName,LastName FROM Person.Person WHERE LastName LIKE 'Ma%'
Both of these queries produce the same result but the first one is non-sargable and will run little slow compared to the second one which is sargable.
Reference : Vijaya Kadiyala (www.DotNetVJ.com)
Tuesday, February 9, 2010
DATEDIFF Function in SQL Server
In this post i would like to show you to find the difference between two dates using DATEDIFF in SQL Server.
Syntax: DateDiff(DatePart, StartDate, EndDate)
DatePart is the parameter on which SQL Server calculates the difference between two input dates i.e. startdate and enddate.
Please refer to the below table:
Datepart Abbreviations
| DatePart | Abbreviations |
|---|---|
| Year | yy, yyyy |
| quarter | qq, q |
| Month | mm, m |
| dayofyear | dy, y |
| Day | dd, d |
| Week | wk, ww |
| Hour | hh |
| minute | mi, n |
| second | ss, s |
| millisecond | ms |
Ex: To calculate the difference between two dates (No Of Days)
SELECT DATEDIFF(DAY,'2001-01-01','2010-01-01') AS No_Of_Days_Difference
Output:
No_Of_Days_Difference
---------------------
3287
Ex: To calculate the difference between two dates (No Of Years)
SELECT DATEDIFF(YEAR,'2001-01-01','2010-01-01') AS No_Of_Years_Difference
Output:
No_Of_Years_Difference
---------------------
9
Ex: To calculate the difference between two dates (No Of Months)
SELECT DATEDIFF(MONTH,'2001-01-01','2010-01-01') AS No_Of_Months_Difference
Output:
No_Of_Months_Difference
---------------------
108
Reference : Vijaya Kadiyala(www.DotNetVJ.com)
Monday, February 8, 2010
DotNetVJ News - 500th Article
This is my 500th article and I very happy and excited about it. I started this blogging on 18-NOV-2007 to share my knowledge and build my own repository of what I am working on. I started this blog on .Net and then slowly started writing articles on SQL Server, PowerShell and MS Office Tips and Tricks. During this course of blogging i was awarded Microsoft Most Valuable Professional in ASP.NET (2008-2009) and in SQL Server (2009-2010). I am very happy and will continue to share my knowledge.
Thursday, February 4, 2010
Find the Database creation date (DATABASE AGE) in SQL Server
In this post i would like to show you simple tip to find when the database created.
SELECT name,crdate
FROM master..sysdatabases
Database->Date Of Creation
-------------------------------
master-> Apr 8 2003 9:13AM
tempdb-> Jan 29 2010 9:22PM
model-> Apr 8 2003 9:13AM
msdb-> Jul 9 2008 4:46PM
AdventureWorks-> Aug 31 2009 9:49AM
AdventureWorksDW-> Aug 31 2009 9:50AM
AdventureWorksLT-> Aug 31 2009 9:50AM
AdventureWorks2008-> Aug 31 2009 9:50AM
AdventureWorksDW2008-> Aug 31 2009 9:51AM
AdventureWorksLT2008-> Aug 31 2009 9:51AM
(13 row(s) affected)
Please let me know if you have any other way to find the same information...
Wednesday, February 3, 2010
Table Scan Vs Index Scan in SQL Server
Today i would like to clarify the difference between the Index Scan and Table Scan.
A table scan, table is processed row by row from start to end. In the index scan, index is processed row by row from start to end.
If the index is a clustered index then an index scan is really a table scan.
Reference : Vijaya Kadiyala (www.DotNetVJ.com)
Tuesday, February 2, 2010
Convert list of values seperated by comma stored in a column into Multiple Rows in SQL Server
Today, I would like to give you simple tip to convert list of values seperated by comma stored in a column into Multiple Rows in SQL Server.
declare @String varchar(MAX)
set @String = '100,200,250,300,350,450,500'
set @String =','+ @String + ','
SELECT REPLACE(Val_Column,',','')
FROM
(
select
substring(@String,number,CHARINDEX(',',@String,number+1)-number) As Val_Column
from
master..spt_values
where number < LEN(@String)
and type = 'P'
) C
where Val_Column like ',%'
Output
--------------------------------------
100
200
250
300
350
450
500
(7 row(s) affected)
Monday, February 1, 2010
Split Full Name into First Name, Middle Name, Last Name in SQL Server using PARSENAME function
In this post i would like to show you a simple technique to split the full name. There are various techniques available to do the same using LEFT, RIGHT,SUBSTRING, CHARINDEX functions.
DECLARE @SQLVariable VARCHAR(100);
SET @SQLVariable = 'Vijaya.Krishna.Kadiyala.SQL Server';
select PARSENAME(@SQLVariable,1) AS Technical_Skill;
select PARSENAME(@SQLVariable,2) AS LAST_NAME;
select PARSENAME(@SQLVariable,3) AS MIDDLE_NAME;
select PARSENAME(@SQLVariable,4) AS FIRST_NAME;
Output:
Technical_Skill
-----------------
SQL Server
(1 row(s) affected)
LAST_NAME
-------------------
Kadiyala
(1 row(s) affected)
MIDDLE_NAME
-------------------
Krishna
(1 row(s) affected)
FIRST_NAME
-------------------
Vijaya
(1 row(s) affected)
Reference : Vijaya Kadiyala (www.DotNetVJ.com)
Thursday, January 28, 2010
Convert Number to Varchar in SQL Server using CAST or CONVERT or STR or Any other String Functions
Recently i started to explpore "ways" in SQL Server.
Ways in SQL Server:
===============
Implementation of NOT IN operator with out using NOT IN....
TOP 5 ways to delete Duplicate Records in a Table
In the same series today i would like to show you different ways to convert number to varchar.
Using CAST Function:
=================
SELECT CAST(YEAR(GETDATE()) AS VARCHAR)
Output:
----
2010
(1 row(s) affected)
Using CONVERT Function:
======================
SELECT CONVERT(VARCHAR(4),YEAR(GETDATE()))
Output:
----
2010
(1 row(s) affected)
Using STR String Function:
=====================
SELECT STR(YEAR(GETDATE()))
Output:
----
2010
(1 row(s) affected)
Using RTRIM or LTRIM Functions:
=============================
SELECT RTRIM(YEAR(GETDATE()))
Output:
----
2010
(1 row(s) affected)
When you apply any string functions on the numbers then by default SQL Server converts them to string data type.
Please let me know if you have any other ways.....
Related Articles:
============
String Functions in SQL Server Part 1
String Functions in SQL Server -- Final Part
Wednesday, January 27, 2010
Search For Columns in SQL Server
In this post i would like to show you various methods to search for columns in SQL Server metadata tables.
Method 1:
========SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA,
TABLE_NAME,
COLUMN_NAME
FROM
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS
WHERE COLUMN_NAME LIKE
'%emp%';
Method 2:
========SELECT OBJECT_SCHEMA_NAME(object_id) AS SCHEMANAME,
OBJECT_NAME(object_id) OBJECTNAME,
name as column_name
FROM
sys.columns
WHERE name LIKE '%emp%';
I normally use Method 1, to find the information. Please let me know if you have any other approach.....
Tuesday, January 26, 2010
Is Your MONEY Safe in SQL Server
In this post i would like to share my experience with you on MONEY data type in SQL Server .
Let’s looks at one example where MONEY data type will round numbers.
Usage of MONEY data type in storing amounts
DECLARE @Money_Amt1 MONEY, @Money_Amt2 MONEY
SET @Money_Amt1 = 100100.1234567;
SET @Money_Amt2 = 100100.1234;
SELECT @Money_Amt1 AS Money_Amt1,
@Money_Amt2 AS Money_Amt2;

As you can see Money data type can hold only up to 4 digits after the decimal. If you are trying to assign a number whose scale is more than 4 digits, then money data type rounds the number, in which case over the course of the time you will accumulate lot of in correct amounts. So you need to make right decision in choosing the right data type for your data.
FYI: This is not a bug neither this is the limitation.
Let’s look at one example where you want to multiply two MONEY data type variables .
Usage of MONEY data type in Multiplication
DECLARE @Your_Money MONEY, @Currency_Conversion_Rate MONEY;
SET @Your_Money = 12.2345;
SET @Currency_Conversion_Rate = 18.7686;
SELECT (@Your_Money * @Currency_Conversion_Rate) AS Col1,
(@Your_Money * 1.0 * @Currency_Conversion_Rate) AS Col2;
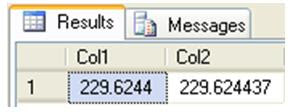
As you can see in the above query, I declared two variables. The result of the multiplication or division of two money data type is always money. As discussed previously money data type can hold only 4 digits after the decimal and if it is anything more than that it tries to round to the nearest number. As you can see in the Col1, you don’t see the accurate results of the multiplication operation and whereas in the Col2 by multiplying with 1.0, basically SQL Server is converting into numeric.
Wednesday, January 20, 2010
Order By Clause is not accepting alias Name in SQL Server
Today, i came across a strange behaviour of ORDER BY clause in SQL Server. In one of my post i mentioned that ORDER BY clause is final step in the SQL Query if you don't have TOP keyword in the query.
Lets look at the below example:
SELECT
BusinessEntityID,
LoginID,
HireDate,
GETDATE() AS Current_Dt
FROM HumanResources.Employee
ORDER BY Current_Dt
In this query i have an alias name in the ORDER BY Clause and SQL Server executes the query with out any errors as shown below:
Now If i use any functions on the alias column in the ORDER BY clause, it comes out with errors:
SELECT BusinessEntityID,
LoginID,
HireDate,
GETDATE() AS Current_Dt
FROM HumanResources.Employee
ORDER BY ABS(DATEDIFF(DAY,Current_Dt,HireDate));
Do let me know if you have any answer to this question....
Reference : Vijaya Kadiyala (www.DotNetVJ.com)
Intellisense update/refresh on schema changes - SQL Server
The intellisense in SQL Server 2008 is a great feature but sometimes you might get into trouble with it. As an example, If you make any change like creating a new table or column name change etc, while SSMS is open those changes are not reflected in current or even new query editor window in that instance of SSMS.
If you close the instance and launch SSMS again then you can see the changes. So for every change you don't want to close and re-open. So here is the tip, Just refresh your local cache then it will work.
You can refresh you local cache by going to Edit->IntelliSense->Refresh Local Cache or simple using short cut (CTRL+Shift+R)
Reference : Vijaya Kadiyala (www.DotNetVJ.com)
Monday, January 18, 2010
Get the records nearest to GETDATE() in SQL Server
In this post i would like to show you different ways to find the rows nearest to the GetDate() in SQL Server.
Method 1, is based on calculating the difference interims of days between GetDate() and HireDate and then take the absolute number using ABS. Order these results in ascending (ASC)order by using ORDER BY Clauase. Finally, filter the results using TOP 1 WITH TIES. WITH TIES is used to select all the records when there is a tie.
Method 1:
=======
SELECT TOP 1 WITH TIES
BusinessEntityID,
LoginID,
HireDate,
GETDATE() AS [Current_Date]
FROM HumanResources.Employee
ORDER BY ABS(DATEDIFF(DAY,GETDATE(),HireDate));
Method 2, is based on using Group Functions. Where MAX function is used to take the recent date and based on this date extracted all the other information.
Method 2:
=======
SELECT
BusinessEntityID,
LoginID,
HireDate
FROM HumanResources.Employee
WHERE HireDate = (SELECT MAX(HireDate) FROM HumanResources.Employee)
Method 3, is based on Analytical Functions in SQL Server. Where RANK function is used to
along with the OVER BY to calculate the difference between GetDate and HireDate. This logic is same as in Method 1.
Method 3:
=======
SELECT V.* FROM
(SELECT
BusinessEntityID,
LoginID,
HireDate,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY ABS(DATEDIFF(DAY,GETDATE(),HireDate))) AS RecID
FROM HumanResources.Employee ) V
WHERE V.RecID = 1
Please let me know if you have any other ways to wirte these queries.....
Reference : Vijaya Kadiyala (http://www.dotnetvj.com/)
Saturday, January 16, 2010
DROP INDEX - Must specify the table name and index name for the DROP INDEX statement
In this post i would like to show you, how to drop an index in SQL Server.
If you came from different database backgrounds like Oracle or DB2, then you will issue the following statement and expect to execute without errors.
DROP INDEX INDEX_NAME
This will not work in SQL Server. You need to specify the on which table this index is defined.
When you execute the above statement you will get below error:
Msg 159, Level 15, State 1, Line 1
Must specify the table name and index name for the DROP INDEX statement.
The right way to drop an index is:
DROP INDEX INDEX_NAME
Related Articles:
Clustered Index in SQL Server
Non Clustered Index in SQL Server
Covering Index in SQL Server
Filtered indexes in SQL Server 2008
Reference: Vijaya Kadiyala (www.DotNetVJ.com)
Friday, January 15, 2010
When to use fully qualified names in SQL Server
In Sql Server each and every object name has four parts.
1. Server Name
2. Database Name
3. Owner Name
4. Object Name
If you quality Object Name with Server Name, Database Name and Owner then it is referred as Fully Qualified Name.
Some people believes that if you fully qualify the object name it will improve the performance. But its not true. Depends on the need you need to make a right choice. As an example if your application is using one/single database always then you can write queries as shown below:
SELECT * FROM HumanResources.ShiftSometimes owner name is also referred as Schema. If you take AdventureWorks2008 database, then there are various schemas like HumanResources, Sales, Production, Person etc.
If you have multiple databases and your queries always joins two or more tables from two or more different databases then it will be good if you qualify with database name as shown below:
VJ_LCL is my local database and the schema owner of emp table is dbo. Similarly AdventureWorks2008 is database and HumanResources is the schema name and Shift is the table name. Rememeber, object name has to be unique within each schema.SELECT * FROM
AdventureWorks2008.HumanResources.ShiftSELECT * FROM
VJ_LCL.dbo.emp
On the other hand, if you have queries that has joins between two or more tables from two or more different servers then you need to fully qualify the object name as show below:
SELECT * FROM
VJMSSQLServer.AdventureWorks2008.HumanResources.Shift
If you fully qualify each and every object even when you have single database then you might get into following problems:
1) If you are planning to change the database, your code will break
2) If you are planning to change the server or deploying it on another server then your code will break.
Reference: Vijaya Kadiyala (http://DotNetVJ.com)
Getting the Server Name in SQL Server using @@SERVERNAME
In this post i would like to give you a simple tip on how to get the Server Name of the SQL server.
In order to get the SQL Server - Server name you need to use Global Variable as shown below.
SELECT @@SERVERNAME AS Server_Name
Thursday, January 14, 2010
Get Current date and time in SQL Server using CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, GETDATE(), SYSDATETIME()
In this post i would like to discuss with you about displaying current date and time in SQL Server.
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP is ANSI compliant. This value is based on the operating system where the SQL Server instance is running. This function is nondeterministic function.
GETDATE() is inherited from sybase.
SYSDATETIME(), this value is based on the operating system where the SQL Server instance is running. This function is nondeterministic function. The return type of this function is datetime2. So this is more accurate than any other time based function.
In addition to this there is another way to display the current date and time.
The {fn Now()} is an ODBC canonical function which can be used in T-SQL. There is no performance difference between any of these functions.
SELECT SYSDATETIME() AS "SYSDATETIME",
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP AS "CURRENT_TIMESTAMP",
GETDATE() AS "GETDATE",
{fn NOW()} AS "fn_now()"






